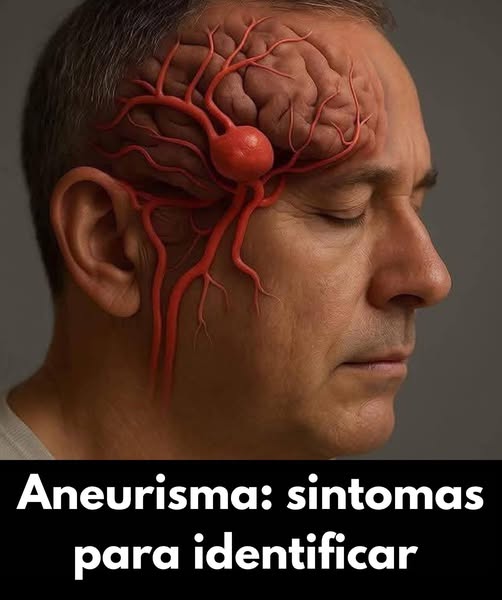
An aneurysm can go unnoticed, but it can also cause serious emergencies. Learn what it is, its causes, and the warning signs.
You’ve heard of an aneurysm , but you might not know exactly what it is — it just sounds like something serious.
And it is indeed.
But understanding how it arises, when it manifests, and what to do about it can take away the fear and put the necessary attention in its place.
The good news?
Not every aneurysm is a serious sentence. But knowing how to identify the right signs at the right time can make all the difference.

What is an aneurysm, anyway?
Think of a balloon forming in the wall of an artery. This is an aneurysm: an abnormal, localized dilation of a blood vessel, usually caused by a weakening of the arterial wall.
It can form in various parts of the body, but the most common ones occur:
- In the brain (brain aneurysm)
- In the abdominal or thoracic aorta (the body’s main artery)
The main risk is a ruptured aneurysm , which can cause severe internal bleeding — a medical emergency.
What causes an aneurysm?
Some people are born with a predisposition. Others develop it over time, due to vascular wear. The most common factors are:
- High blood pressure (hypertension): constant force against the artery wall can deform it
- Atherosclerosis: Fat accumulation hardens and weakens blood vessels
- Smoking: directly damages vascular walls
- Family history: those with cases in the family are at greater risk
- Trauma or infections: can directly affect the structure of the vessels
Can you feel that you have an aneurysm?
Unfortunately, not in most cases . Many aneurysms remain “silent” for years. However, some signs may appear when the aneurysm grows or threatens to rupture:
- Sudden and intense pain , depending on the affected area (head, abdomen, chest)
- Dizziness or fainting
- Blurred or double vision
- Abnormal pulsation in the abdomen
- Intense and unexplained fatigue
When an aneurysm ruptures: emergency signs
If this happens, the body reacts drastically. A rupture is a critical situation that requires immediate attention . The symptoms are intense and often unmistakable:
- Unbearable pain (like an internal “explosion”)
- Sudden loss of consciousness
- Difficulty speaking, walking, or moving one side of the body
- Drop in blood pressure and irregular breathing
If you witness this in someone, call SAMU (192) immediately.
When to see a doctor?
Even without symptoms, it’s worth paying attention if you:
-
- Have a family history of aneurysms or strokes
- Are you hypertensive or a chronic smoker?
- He is over 50 years old and has never had vascular exams.
Tests such as ultrasound, CT angiography or magnetic resonance imaging can detect aneurysms early.
Is it possible to prevent an aneurysm?
It’s not possible to completely prevent it, but it is possible to greatly reduce the risk with daily care:
-
- Control your blood pressure with diet and, if necessary, medication.
- Stop smoking : cigarettes are one of the biggest vascular aggressors
- Practice light to moderate physical activity regularly
- Have a balanced diet : less salt and fat, more vegetables and fiber
- Avoid excess alcohol and control cholesterol
- Get annual checkups , especially if you have risk factors.

FAQ
What exactly is an aneurysm?
It’s an abnormal dilation of an artery caused by weakening of the vessel wall. It can occur in the brain, aorta, or other areas.
Do aneurysms cause symptoms?
Not always. Many are silent until they grow too large or rupture. But sudden, intense pain can be a warning sign.
How can I tell if I have an aneurysm?
Only with tests like CT scans or ultrasounds. If there’s a family history or risk factors, it’s worth investigating.
Does every aneurysm require surgery?
No. Most small aneurysms require monitoring only. Surgery is indicated when there is a risk of rupture.
Knowing what an aneurysm is shouldn’t scare you — it should make you more aware.
The secret lies in prevention, observation and quick action when signs appear.
Because when it comes to vascular health, every second matters.