Our body has a remarkable way of alerting us when something is wrong and requires attention. These alerts often come in the form of symptoms — pain, dizziness, tingling, or numbness — signaling that it’s time to seek medical help.
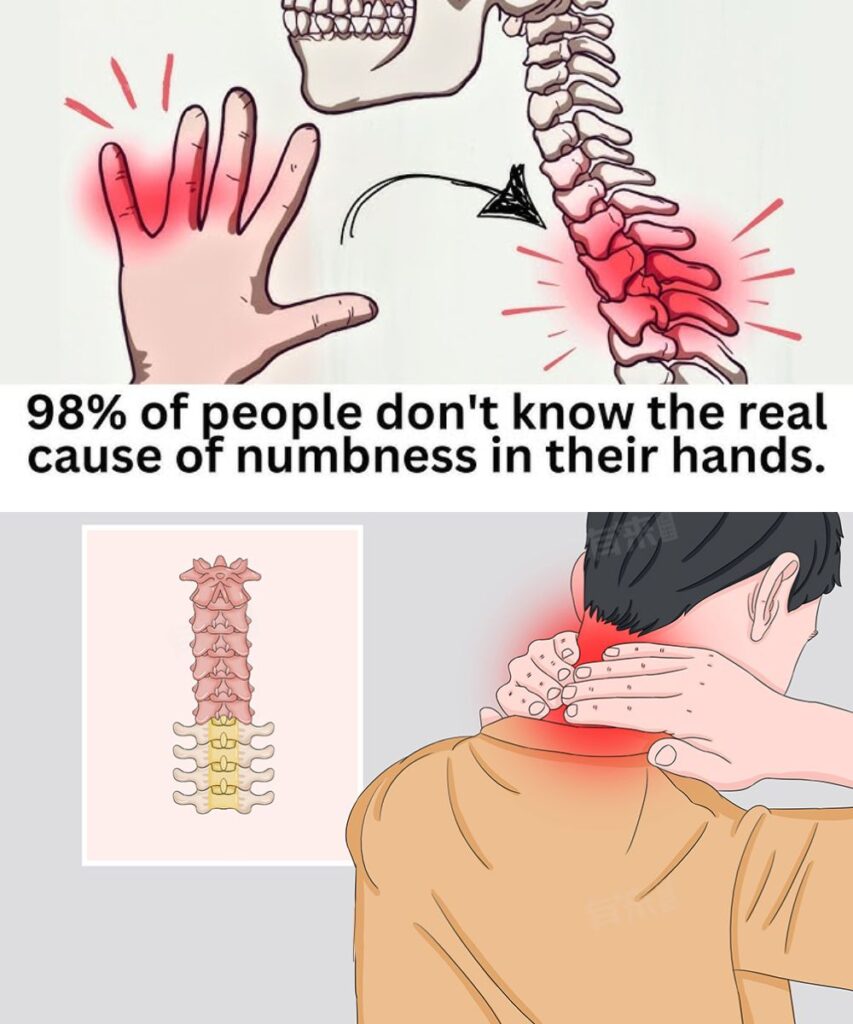
One symptom that should never be ignored is numbness or tingling in the hands. This sensation often means the affected area is not receiving enough blood flow or nerve signals. Let’s explore the possible causes, when to worry, and how to get the right diagnosis.
Why Do Your Hands Go Numb?
In many cases, numbness in the hands is caused by poor circulation, affecting areas from the palm to the fingertips. Ignoring this warning sign could lead to serious health complications. Below are the most common causes:
1. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
This degenerative disease damages the spinal cord and disrupts the nervous system’s ability to send messages. Tingling or numbness in the hands can be one of its early symptoms.
2. Cervical Osteochondrosis
A spinal condition that affects the neck region, blocking or reducing blood flow to the arms and hands. It can lead to persistent numbness and discomfort.
3. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
A common issue for people who perform repetitive hand movements — such as excessive typing or playing musical instruments. It happens when the median nerve in the wrist is compressed.
4. Blood Clots and Stroke
A blood clot (thrombosis) in a vein can block circulation and cause sudden numbness. Likewise, a stroke can also trigger hand numbness, often accompanied by other symptoms like weakness or difficulty speaking. These are medical emergencies requiring immediate attention.
5. Buerger’s Disease
Mostly affecting smokers, this rare condition restricts blood flow to the limbs, sometimes leading to gangrene if untreated.
6. Diabetes
High blood sugar damages nerves over time, causing diabetic neuropathy, which often begins with tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
When to See a Doctor
If you frequently experience numbness or tingling in your hands, consult a healthcare provider. Early intervention can prevent long-term nerve damage or serious complications.
How Doctors Diagnose the Cause
A thorough diagnosis usually involves:
-
- Medical consultation – reviewing symptoms, health history, and risk factors.
-
- Physical examination – checking reflexes, strength, and nerve sensitivity.
- Blood tests – to assess glucose, thyroid function, and electrolyte balance.
- Imaging tests – X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI to examine the neck, nerves, and blood vessels.
- Neurological tests – to evaluate nerve function and conduction speed.
Treatment Options
Depending on the underlying cause, treatment may include:
-
- Medications to reduce inflammation or manage pain
-
- Physical therapy to improve movement and posture
- Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and improving diet
- Surgery for severe nerve compression cases
Bottom Line
Numbness in the hands is not just a minor inconvenience — it can be an early sign of serious health problems. By recognizing the warning signs and seeking prompt medical advice, you can protect your circulation, preserve nerve function, and safeguard your overall health.
Our body has a remarkable way of alerting us when something is wrong and requires attention. These alerts often come in the form of symptoms — pain, dizziness, tingling, or numbness — signaling that it’s time to seek medical help.
One symptom that should never be ignored is numbness or tingling in the hands. This sensation often means the affected area is not receiving enough blood flow or nerve signals. Let’s explore the possible causes, when to worry, and how to get the right diagnosis.
Why Do Your Hands Go Numb?
In many cases, numbness in the hands is caused by poor circulation, affecting areas from the palm to the fingertips. Ignoring this warning sign could lead to serious health complications. Below are the most common causes:
1. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
This degenerative disease damages the spinal cord and disrupts the nervous system’s ability to send messages. Tingling or numbness in the hands can be one of its early symptoms.
2. Cervical Osteochondrosis
A spinal condition that affects the neck region, blocking or reducing blood flow to the arms and hands. It can lead to persistent numbness and discomfort.
3. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
A common issue for people who perform repetitive hand movements — such as excessive typing or playing musical instruments. It happens when the median nerve in the wrist is compressed.
4. Blood Clots and Stroke
A blood clot (thrombosis) in a vein can block circulation and cause sudden numbness. Likewise, a stroke can also trigger hand numbness, often accompanied by other symptoms like weakness or difficulty speaking. These are medical emergencies requiring immediate attention.
5. Buerger’s Disease
Mostly affecting smokers, this rare condition restricts blood flow to the limbs, sometimes leading to gangrene if untreated.
6. Diabetes
High blood sugar damages nerves over time, causing diabetic neuropathy, which often begins with tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
When to See a Doctor
If you frequently experience numbness or tingling in your hands, consult a healthcare provider. Early intervention can prevent long-term nerve damage or serious complications.
How Doctors Diagnose the Cause
A thorough diagnosis usually involves:
-
- Medical consultation – reviewing symptoms, health history, and risk factors.
-
- Physical examination – checking reflexes, strength, and nerve sensitivity.
- Blood tests – to assess glucose, thyroid function, and electrolyte balance.
- Imaging tests – X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI to examine the neck, nerves, and blood vessels.
- Neurological tests – to evaluate nerve function and conduction speed.
Treatment Options
Depending on the underlying cause, treatment may include:
-
- Medications to reduce inflammation or manage pain
-
- Physical therapy to improve movement and posture
- Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and improving diet
- Surgery for severe nerve compression cases
Bottom Line
Numbness in the hands is not just a minor inconvenience — it can be an early sign of serious health problems. By recognizing the warning signs and seeking prompt medical advice, you can protect your circulation, preserve nerve function, and safeguard your overall health.