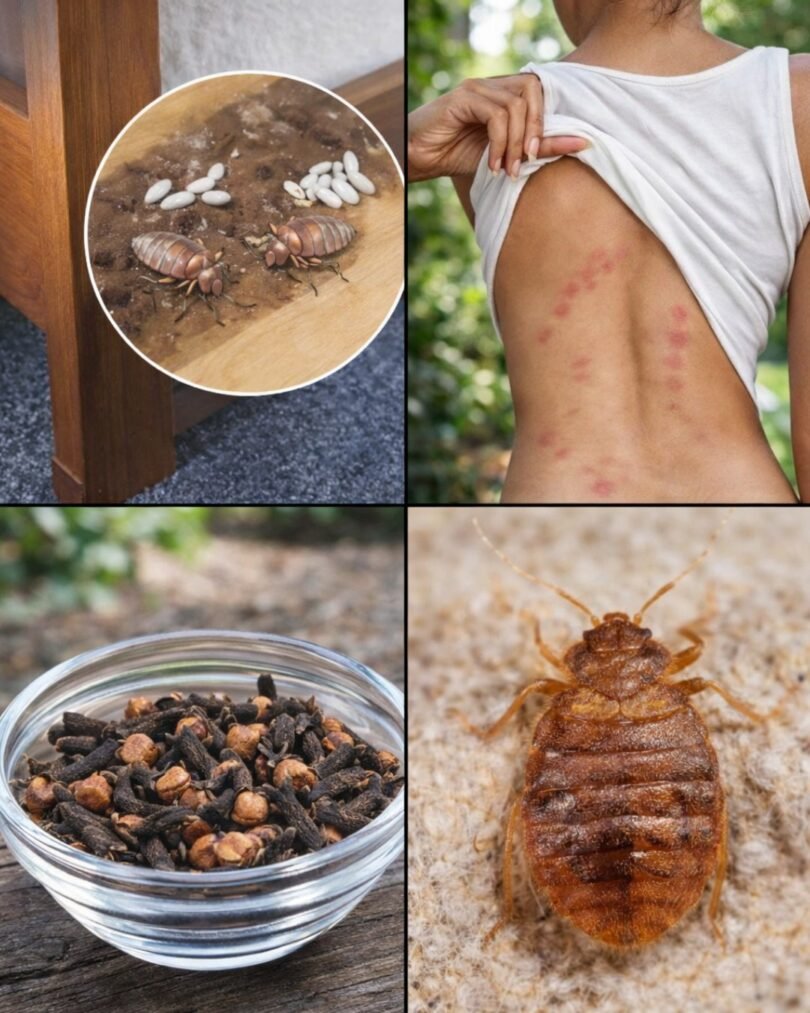
Waking up to itchy, red bites in straight lines or clusters can turn your peaceful bedroom into a source of constant frustration and sleepless nights. These tiny invaders hide in the smallest cracks during the day, only emerging at night to feed, leaving behind not just physical discomfort but also stress and embarrassment as they spread quickly through homes. The good news is that with consistent effort and the right steps, many people successfully manage and reduce bed bug populations in their living spaces.
In this guide, we’ll explore how bed bugs survive and thrive, plus practical steps you can take right away. But here’s the surprising part most people miss: one common household spice often pops up in home remedy discussions—stay tuned to see if it truly helps or if it’s just a myth.

Understanding Bed Bugs: How They Live and Survive
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, flat, reddish-brown insects about the size of an apple seed when adults. They don’t fly or jump but crawl quickly, hitching rides on luggage, clothing, or furniture.
These pests are nocturnal, preferring to feed on human blood while you sleep. Research from pest control authorities shows they can survive months without a meal, making them incredibly resilient in hidden spots.
Life Cycle of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs go through several stages:
- Eggs: Tiny, pearl-white, and sticky, often laid in clusters in mattress seams or cracks. They hatch in about 6-10 days.
- Nymphs: Young bed bugs molt five times, needing a blood meal each time to grow. They start translucent and become darker after feeding.
- Adults: Females lay 1-10 eggs per day, up to 500 in a lifetime under ideal conditions.
This rapid reproduction explains why small infestations can explode quickly if not addressed early.
Here’s a quick comparison of bed bug stages for easy identification:
- Egg — Pinhead-sized, white, stuck to surfaces
- Nymph (young) — Smaller than adults, pale or translucent until fed
- Adult — Flat, oval, 4-5 mm long, turns reddish after feeding
But that’s not all… their hiding habits make them masters of survival.

Where Bed Bugs Hide and Why They’re So Hard to Spot
Bed bugs love warm, dark crevices near sleeping areas. Common spots include:
- Mattress seams, tags, and piping
- Box spring crevices
- Bed frame cracks and headboards
- Baseboards, electrical outlets, and furniture joints
- Even inside walls or behind wallpaper in severe cases
They leave clues like small dark fecal spots (like pepper flakes), shed skins, and a faint musty odor. Studies indicate early detection through thorough inspections dramatically improves control outcomes.
The problem intensifies because they spread easily—via travel bags, second-hand furniture, or even shared laundry.

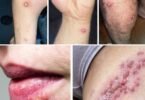
Signs You Might Have Bed Bugs (And What Bites Look Like)
Many people first notice bed bug issues through skin reactions. Bites often appear as:
- Red, itchy welts in lines, zigzags, or clusters (sometimes called “breakfast, lunch, dinner”)
- Raised bumps that may blister or swell
Reactions vary—some people show no marks, while others develop strong irritation. Remember, similar symptoms can come from other sources, so finding actual bugs or signs confirms the issue.
If you’re dealing with these frustrating marks, you’re not alone. Many homeowners face this challenge, but taking action early makes a big difference.
Effective Steps to Reduce Bed Bugs in Your Home
Eliminating bed bugs requires patience and an integrated approach. Authorities like the EPA recommend combining non-chemical methods with careful monitoring.
Step-by-Step Actionable Guide
- Inspect Thoroughly
Check mattresses, furniture, and nearby areas. Use a flashlight to look for bugs, eggs, or spots. - Contain the Problem
Seal infested items in plastic bags. Avoid moving things to other rooms. - Clean and Heat-Treat
Wash bedding and clothes in hot water, then dry on high heat (at least 130°F for 40+ minutes). Vacuum thoroughly, sealing and discarding the bag outside. - Use Protective Measures
Encase mattresses and box springs in bed bug-proof covers (leave on for at least a year). Place interceptors under bed legs to trap crawling bugs. - Apply Non-Chemical Controls
Steam clean fabrics and cracks (ensure 130°F+ temperature). Consider desiccants like EPA-registered diatomaceous earth in hidden areas (they dehydrate bugs over time). - Monitor Progress
Check traps weekly. Repeat steps as needed—eggs can hatch later.
Many sources emphasize that heat and thorough cleaning form the foundation of success, as bed bugs die at sustained high temperatures.

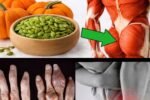
Natural Options: Can Cloves Really Help Against Bed Bugs?
Cloves and clove oil often appear in online discussions as a natural deterrent due to their strong scent and eugenol content. Some lab studies show certain essential oil compounds, including eugenol from cloves, can affect insects when applied directly.
However, reliable pest control information indicates cloves or whole dried cloves placed around beds act mainly as a mild repellent at best—they don’t reliably kill bugs or eggs in an active infestation.
Quick Pros and Cons of Using Cloves:
- Pros — Natural, pleasant aroma, inexpensive
- Cons — Limited evidence for full control, won’t eliminate hidden populations
This is the part many overlook: while cloves might discourage bugs in some spots, they’re no substitute for proven steps like heat treatment and encasements.
For visual reference, here are realistic photos showing whole dried cloves and a close-up of clove oil preparation—simple everyday items people sometimes try for prevention.
(These show natural, handheld smartphone-style shots of dried cloves in a bowl and a small preparation setup under soft natural light.)
When to Seek Professional Help
If your efforts don’t show progress after weeks, or the problem spreads, consider licensed pest management professionals. They use targeted methods for thorough results.
Conclusion: Stay Vigilant for Long-Term Peace
Bed bugs live by hiding, feeding at night, and reproducing quickly—but consistent inspection, cleaning, heat, and protective barriers help many people reclaim their homes. Prevention is key: inspect travel items and used furniture.
FAQ
How long can bed bugs live without food?
They survive several months, sometimes up to a year, in ideal hiding spots.
Do bed bugs spread diseases?
No known disease transmission to humans, though bites cause irritation.
Can I prevent bed bugs when traveling?
Yes—keep luggage elevated, inspect rooms, and wash clothes on high heat upon return.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional pest management advice. Results vary, and persistent issues should be addressed by qualified experts. Consult reliable sources like the EPA for the latest guidance.