23 Subtle Signs Your Kidneys Might Be in Trouble (And You Probably Ignore Them)
Imagine starting each day feeling a little more tired than usual. You brush it off—maybe it’s just another hectic week. But what if that constant fatigue was your kidneys quietly asking for help?
According to the National Kidney Foundation, over 37 million U.S. adults have chronic kidney disease (CKD). Yet, 90% don’t know until the later stages—when treatment choices are limited. Your kidneys quietly filter toxins, balance fluids, and keep electrolytes steady. When they falter, the signs are often so small they get mistaken for everyday issues.
If you’ve followed our Health Hub Fanpage, you’ve seen us explore “hidden health red flags” that spark curiosity. This guide breaks down 23 often-overlooked symptoms of kidney trouble—based on trusted sources like the Mayo Clinic and Kidney.org—plus real-life examples and practical tips.
Urinary Changes You Shouldn’t Ignore
1. Foamy or Bubbly Urine
Persistent bubbles after flushing could mean protein is leaking into your urine—a sign your kidney filters are stressed.
💡 Tip: Keep a hydration diary to tell dehydration from kidney issues.
2. Frequent Nighttime Urination (Nocturia)
Needing to pee more than once or twice at night may indicate kidneys struggling to concentrate urine.
💡 Tip: Limit evening fluids and track frequency for a week.
3. Blood in Urine (Hematuria)
Pink, red, or cola-colored urine can mean inflammation, stones, or infection.
💡 Tip: Use home test strips for a quick check, but see a doctor promptly.
4. Reduced Urine Output
Producing noticeably less urine despite normal hydration can signal reduced kidney function.
💡 Tip: Use apps to log intake/output for patterns.
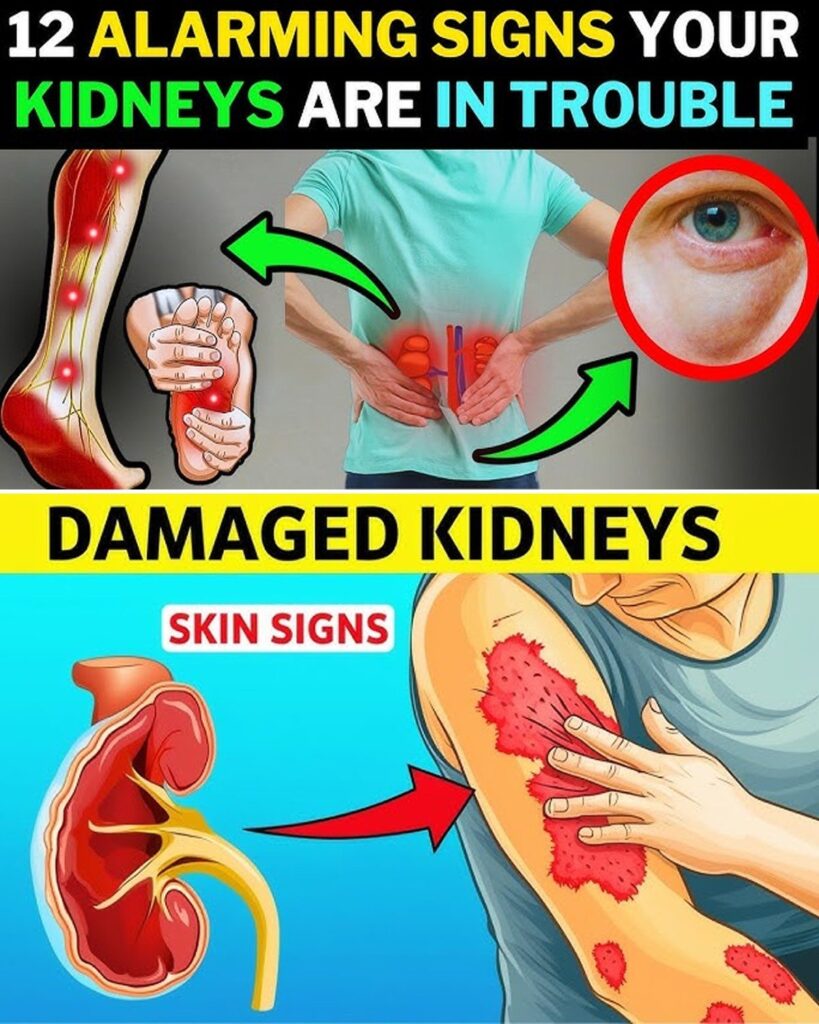
Changes in Skin and Appearance
5. Dry, Itchy Skin
Could be from toxin buildup or mineral imbalance in later CKD stages.
💡 Tip: Moisturizers help, but a blood test is key.
6. Swelling in Feet, Ankles, or Hands
Excess sodium can cause fluid retention.
💡 Tip: Elevate legs and reduce salt to ease puffiness.
7. Morning Eye Puffiness
Often linked to protein loss in urine.
💡 Tip: Cold compresses soothe, but watch for patterns.
8. Pale or Yellowish Skin Tone
Low red blood cell production and toxin buildup can alter skin color.
💡 Tip: Add iron-rich foods after testing.
Energy, Mood, and Mental Clarity
9. Constant Fatigue
Anemia and toxin overload can make you feel drained.
💡 Tip: Balanced meals and light activity may help—but check labs.
10. Brain Fog
Trouble focusing or forgetfulness can come from waste buildup.
💡 Tip: Brain games help, but medical checks are essential.
11. Sleep Disturbances
Itching, cramps, or hormone changes may disrupt rest.
💡 Tip: Create a calming bedtime routine.
12. Muscle Cramps
Mineral imbalances, like low calcium, can cause nighttime cramps.
💡 Tip: Stretch before bed and review electrolytes.
Digestive and Appetite Clues
13. Loss of Appetite
Metallic taste or nausea from toxin buildup can dull hunger.
14. Nausea or Vomiting
Uremia can feel like morning sickness—outside of pregnancy.
15. Metallic Taste in Mouth
High blood urea changes how food tastes.
16. Abdominal Bloating or Pain
Fluid buildup or infection can mimic digestive troubles.
Other Overlooked Signs
17. Shortness of Breath
Fluid in lungs or anemia reduces oxygen supply.
18. Persistent Back Pain
Ache near the lower ribs could be kidney-related.
19. Sudden Blood Pressure Spikes
Hypertension both causes and worsens kidney damage.
20. Frequent Headaches
Linked to vascular changes and high blood pressure.
21. Unexplained Weight Loss
Nutrient absorption drops as kidney health declines.
22. Bone Pain or Weakness
Mineral loss can weaken bones over time.
23. Irregular Heartbeat
Electrolyte shifts can disturb heart rhythm.
Why These Signs Matter
Kidney disease often mimics minor, unrelated issues until it’s advanced. Recognizing changes early means you can get simple blood or urine tests that may prevent dialysis or transplant later.
FAQ: Kidney Health Basics
Q: What causes kidney disease?
A: Common causes include diabetes, high blood pressure, and infections.
Q: Can it be prevented?
A: Yes—through healthy eating, hydration, blood pressure control, and regular screenings.
Q: Can kidney disease be reversed?
A: Early stages can improve with lifestyle changes; later stages require ongoing management.
Q: What should I do if I have several symptoms?
A: Book a medical checkup for professional evaluation—avoid self-diagnosis.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.